From Extrapolation to Generalization: How Conditioning Transforms Symmetry Learning in Diffusion Models
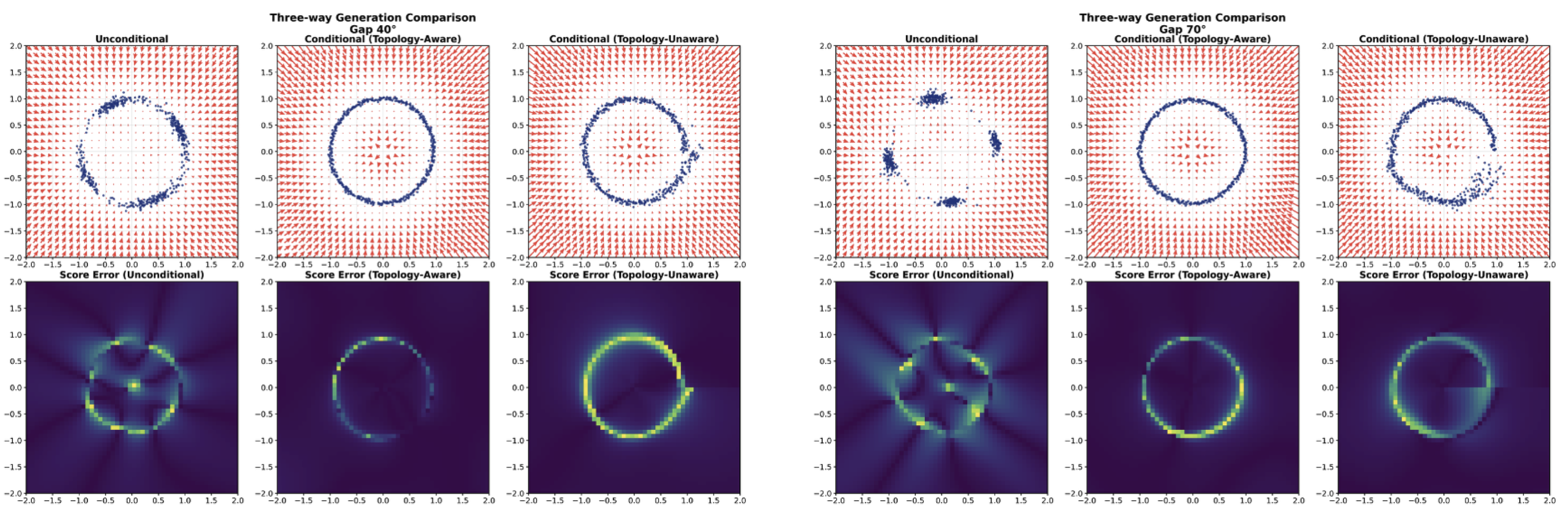 Conditioning on group elements factorizes symmetry learning into low-dimensional function generalization, yielding dramatic improvements on held-out symmetries.
Conditioning on group elements factorizes symmetry learning into low-dimensional function generalization, yielding dramatic improvements on held-out symmetries.
When trained on data with missing symmetries, diffusion models face a fundamental challenge: how can they generate samples respecting symmetries they have never observed? We prove that this failure stems from the structure of the learning problem itself. Unconditional models must satisfy a global equivariance constraint, coupling all group elements into a single optimization that requires high-dimensional data extrapolation across gaps. In contrast, conditioning on group elements factorizes this into independent problems, transforming the task into low-dimensional function generalization. Our theory predicts—and experiments confirm—that this simple change yields 5-10× error reduction on held-out symmetries. On synthetic 2D rotation tasks, conditional models maintain low error even with 300° gaps while unconditional models collapse catastrophically. We further suggest that topology-aware group embeddings may help improve this generalization by ensuring smoother functions over the group manifold.
Sid Bharthulwar, T. Anderson Keller, Manos Theodosis, Demba E. Ba
Accepted at Symmetry and Geometry in Neural Representations (NeurReps) @ NeurIPS 2025 (Poster)
Paper: https://openreview.net/forum?id=UI82R3lwar